What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) to understand customer questions and automate responses to them, simulating human conversation.
AI for Customer Service – IBM Watson users achieved a 337% ROI over three years. Improve the customer experience with conversational AI.
Learn more
The value of chatbots
Chatbots can make it easy for users to find the information they need by responding to their questions and requests—through text input, audio input, or both—without the need for human intervention.
Chatbot technology is almost everywhere these days, from the smart speakers at home to messaging applications in the workplace. The latest AI chatbots are often referred to as “virtual assistants” or “virtual agents.” They can use audio input, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa, or interact with you via SMS text messaging. Either way, you’re able to ask questions about what you need in a conversational way, and the chatbot can help refine your search through responses and follow-up questions.
Featured products
IBM Watson Assistant
IBM Cloud Pak for Data
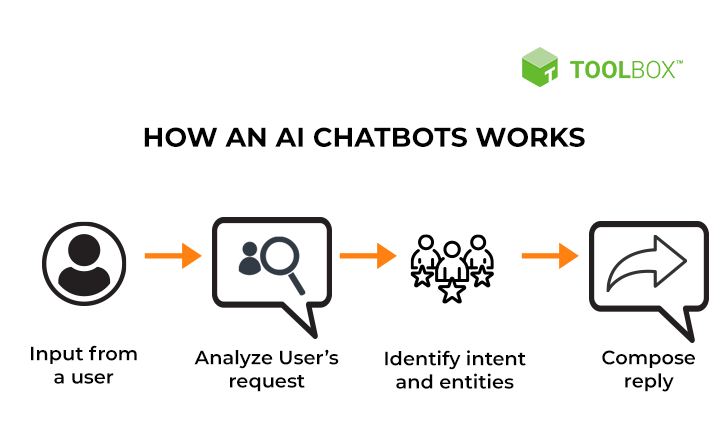
How chatbots work
Historically, chatbots were text-based, and programmed to reply to a limited set of simple queries with answers that had been pre-written by the chatbot’s developers. They operated like an interactive FAQ, and while they worked well for those specific questions and answers on which they had been trained, they failed when presented with a complex question or one that hadn’t been predicted by the developers.
Over time, chatbots have integrated more rules and natural language processing, so end users can experience them in a conversational way. In fact, the latest types of chatbots are contextually aware and able to learn as they’re exposed to more and more human language.
Today’s AI chatbots use natural language understanding (NLU) to discern the user’s need. Then they use advanced AI tools to determine what the user is trying to accomplish. These technologies rely on machine learning and deep learning—elements of AI, with some nuanced differences—to develop an increasingly granular knowledge base of questions and responses that are based on user interactions. This improves their ability to predict user needs accurately and respond correctly over time.
For example, if a user asks about tomorrow’s weather, a traditional chatbot can respond plainly whether it will rain. An AI chatbot, however, might also inquire if the user wants to set an earlier alarm to adjust for the longer morning commute (due to rain).
Related links
How to build a chatbot
Chatbots vs. AI chatbots vs. virtual agents
You may notice the terms chatbot, AI chatbot and virtual agent being used interchangeably at times. And it’s true that some chatbots are now using complex algorithms to provide more detailed responses.
However, it is worth noting that the deep learning capabilities of AI chatbots enable interactions to become more accurate over time, building a web of appropriate responses via their interactions with humans. The longer an AI chatbot has been in operation, the stronger its responses become. So an AI chatbot using deep learning may provide a more detailed and accurate response to a query, and especially to the intentions behind the query, than a chatbot with recently integrated algorithm-based knowledge.
Common chatbot uses
Consumers use AI chatbots for many kinds of tasks, from engaging with mobile apps to using purpose-built devices such as intelligent thermostats and smart kitchen appliances. Business use is equally varied. Marketers use AI chatbots to personalize customer experiences, IT teams use them to enable self-service, and customer contact centers rely on chatbots to streamline incoming communications and direct customers to resources.
Conversational interfaces can vary, too. AI chatbots are commonly used in social media messaging apps, standalone messaging platforms, or applications on websites. Some typical use cases include:
Finding local restaurants and providing directions
Defining fields within forms and financial applications
Getting answers to healthcare questions and scheduling appointments
Receiving general customer service help from a favorite brand
Setting a reminder to do a task based on time or location
Displaying real-time weather conditions and relevant clothing recommendations
Benefits of chatbots
The latest AI chatbots process the data within human language to deliver highly personalized experiences, creating clear benefits for businesses and customers.
Improve customer engagement and brand loyalty
Before the mature e-commerce era, customers with questions, concerns or complaints had to email or call a business for a response from a human. But staffing customer service departments to meet unpredictable demand and retraining staff to provide consistent replies to similar or repetitive queries, day or night, is a constant and costly struggle for many businesses.
Today, chatbots can consistently manage customer interactions 24×7 while continuously improving the quality of the responses and keeping costs down. Chatbots automate workflows and free up employees from repetitive tasks. A chatbot can also eliminate long wait times for phone-based customer support, or even longer wait times for email, chat and web-based support, because they are available immediately to any number of users at once. That’s a great user experience—and satisfied customers are more likely to exhibit brand loyalty.
Reduce costs and boost operational efficiency
Staffing a customer support center day and night is expensive. And for some departments, such as human resources, it might not be possible. Industries have been created to address the outsourcing of this function, but that carries significant cost. It also reduces control over a brand’s interaction with its customers.
A chatbot, however, can answer questions 24 hours a day, seven days a week. It can provide a new first line of support, supplement support during peak periods, or offer an additional support option. At the very least, using a chatbot can help reduce the number of users who need to speak with a human, which can help businesses avoid scaling up staff due to increased demand or implementing a 24-hour support staff.
Generate leads and satisfy customers
Chatbots can help with sales lead generation and improve conversion rates. For example, a customer browsing a website for a product or service may have questions about different features, attributes or plans. A chatbot can provide these answers, helping the customer decide which product or service to buy or take the next logical step toward that final purchase. And for more complex purchases with a multistep sales funnel, the chatbot can qualify the lead before connecting the customer with a trained sales agent.
Best practices and tips for selecting chatbots
Selecting a chatbot platform can be straightforward and the payoff can be significant for companies and users. Providing customers with a responsive, conversational channel can help your business meet expectations for immediate and always-available interactions while keeping costs down.
For example, an e-commerce company could deploy a chatbot to provide browsing customers with more detailed information about the products, highlight differences between models, and offer additional user guides and how-to videos. Likewise, the HR department in an enterprise organization may ask a developer to find a chatbot that can give employees 24/7 access to information about benefits and facilitate navigating that information — all without having to speak with someone in person.
Whatever the case or project, here are five best practices and tips for selecting a chatbot platform.
Pick a solution that can accomplish your immediate goals but won’t limit future expansion. Why does a team want its own chatbot? How is this goal currently addressed, and what are the challenges that are driving the need for a chatbot? How could other groups in your organization also use this technology for their needs, including agent assistance, internal IT or HR support, and even health benefits enrollment?
Understand the impact AI has on the customer experience. Like many buzzwords, AI gets thrown around, so figure out where and how AI is used. It should be helping understand what customers are trying to do and making sense of the various ways that can be expressed as well as helping manage conversations in a natural, non-robotic way. The goal is to get the customer to the information they need without running into any dead ends. Without this, it’s just another FAQ.
Ask what it takes to build, train and improve your chatbot over time. Despite the hype, AI doesn’t come knowing everything you need it to do, so get a clear sense of what intents (goals) or prebuilt content comes out-of-the-box and what you need to create yourself. Some chatbots offer the ability to use historical chatlogs and transcripts to create these intents, saving time. Those using machine learning can also automatically adjust and improve responses over time.
Look for ways to connect to, not replace, existing investments. Often, emerging channels or technologies seem like they will replace established ones. But instead, they become just another medium for an organization to manage. A chatbot that connects to these channels and customer case systems can provide the best of both worlds: Modernizing the customer experience while more accurately routing users to the information and individuals that can solve their problems.
Determine if the chatbot meets your deployment, scalability and security requirements. Every organization and industry has its own unique compliance requirements and needs, so it’s important to have those criteria clearly defined. Many chatbots are delivered via the cloud to draw on the learnings and outcomes from other customer conversations, so if you require an on-premises solution or a single tenant environment, the list of available providers is much shorter. It’s also important to understand if and how your data is used, as it can have major impacts in highly regulated industries.