/ France
FRANCE IN TURMOIL
A dog day afternoon in French politics as Macron uses ‘nuclear option’ to raise retirement age
Issued on: 16/03/2023 – 22:23
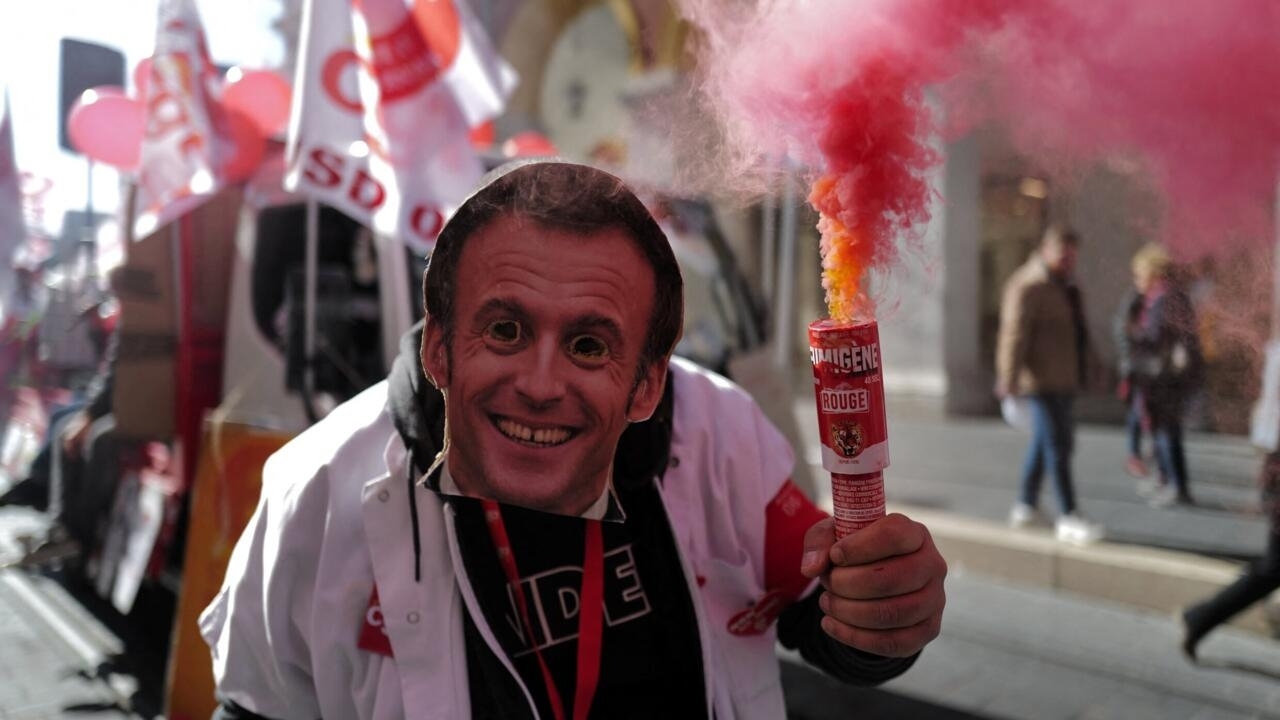
File photo of a demonstrator protesting French President Emmanuel Macron’s pension reform taken in Nice on March 7, 2023.
File photo of a demonstrator protesting French President Emmanuel Macron’s pension reform taken in Nice on March 7, 2023. © Valery Hache, AFP
Text by:
Leela JACINTO
Follow
6 min
France entered a period of political uncertainty on Thursday as French President Emmanuel Macron rammed a controversial pension reform through parliament without a vote by invoking a special executive measure. With the opposition braced for a no-confidence vote and the unions threatening more strikes, France witnessed a dramatic afternoon in politics.
The scenes in the National Assembly, France’s lower house of parliament, on Thursday appeared to have been lifted from historical dramas dating back to the country’s revolutionary past.
“Aux armes citoyens, formez vos bataillons,” sang opposition lawmakers as the chamber echoed with the rallying cry of La Marseillaise, the French national anthem, rallying citizens to take up arms and form battalions. “S’il vous plait, s’il vous plait,” pleaded Yaël Braun-Pivet, the speaker of the National Assembly, ineffectually trying to get order in the house.
Far-left lawmakers in the National Assembly hold placards and sing La Marseillaise, the French national anthem, on March 16, 2023. The placards read “64 years old: No!”
Far-left lawmakers in the National Assembly hold placards and sing La Marseillaise, the French national anthem, on March 16, 2023. The placards read “64 years old: No!” © Pascal Rossignol, Reuters
The session was suspended for two minutes before Prime Minister Élisabeth Borne could announce the triggering of Article 49.3 of the French constitution, which grants the government executive privilege to pass a bill without a vote. Triggering Article 49.3 also permits the opposition to respond with a no-confidence motion.
“Today, we are faced with uncertainty that hinges on a few votes. We cannot take the risk of 175 hours of parliamentary debates collapsing,” said the 61-year-old French prime minister, raising her voice above the din. “On the basis of Article 49.3 of the constitution, I engage the responsibility of my government on the pension reform bill.”
With that, the likely unlikely happened in French politics on Thursday afternoon. President Emmanuel Macron was reelected last year after running on a campaign pledge to raise the retirement age. His reputation as an economic reformer hinged on his ability to make the French work longer by raising the official retirement age from 62, the lowest of any country in the EU.
The French president initially proposed a retirement age of 65, but that was brought down to 64 in January, when he floated the pension reform plan following months of talks with trade unions, employers and political parties.
For Macron, it was the mother of all reforms. For the opposition, particularly the far-left NUPES (New Ecological and Social Popular Union) alliance, it was the mother of all political opposition battles. France’s powerful unions were also on the opposition’s side, and they made it clear with eight nationwide strikes over the past three months, drawing over a million people on the streets almost every week.
While both sides played dare, the threat of Article 49.3 – or simply 49.3 as its popularly known – hung in the air. It was a nuclear option that neither side wanted and few imagined would come to pass. But now that it has, it leaves Macron weakened, Borne particularly vulnerable, and France in a state of shock as the politicians plot their next moves, keeping the country on edge.
An anxious weekend
Under the French constitution, once the prime minister invokes Article 49.3, the opposition has 24 hours to table a motion of censure.
Shortly after Borne’s address in the National Assembly on Thursday, Marine Le Pen said her far-right National Rally party would file a no-confidence motion. Communist lawmaker Fabien Roussel said such a motion is “ready” on the left.
For a no-confidence vote to be put to the chamber, the motion must be signed by at least one-tenth of the National Assembly’s 577 deputies.
Once the no-confidence motion is tabled, the National Assembly has to wait 48 hours before it is discussed in the chamber.
French law provides the 48-hour period to enable the government to convince undecided parties, and to allow lawmakers to make their decision after careful deliberations.
A no-confidence vote requires a majority, which means a minimum of 287 votes.
With a no-confidence motion set to be tabled on Friday, a vote is likely early next week, leaving the French in a state of heightened political anxiety over the weekend. What’s more, by opting for 49.3, Macron may have taken a safe option, but there’s no guarantee it will bring him any peace.
‘Reaping the harvest’ of the 2022 legislative elections
From the onset of the mass mobilisation against the pension reform, Article 49.3 was viewed as a risky option. But with the government unsure of getting the minimum 287 votes in the National Assembly needed to approve the pension bill, Macron chose to play it safe by opting for the nuclear option.
The conservative- dominated Senate approved the reform earlier Thursday in a move that was widely predicted. The political drama was always going to be in the lower house, where the president’s centrist La République en Marche (Renaissance) party does not have a majority.
With just hours to go before the National Assembly vote, Macron held a Cabinet meeting at the Elysée presidential palace to strategise the next move as the country waited with baited breath.
The decision to opt for 49.3 came just a few minutes before the scheduled vote in the National Assembly. The roots of the controversial decision, though, date back to the June 2022 legislative elections, when Macron’s alliance lost its parliamentary majority.
“The president was already weakened when his centrist grouping, Renaissance, failed to gain an absolute majority in the legislative elections back in June,” explained FRANCE 24’s International Affairs Commentator Douglas Herbert. “We’re basically reaping the harvest of the last legislative elections. What we’re seeing right now are the vulnerabilities of a presidential movement or party when it doesn’t have a parliamentary majority.”
Thursday saw the article used for the 100th time under France’s modern constitution, which created an all-powerful president in 1958, overturning the previous one and its parliamentary system.
Under the modern fifth republic, 16 prime ministers have used the article and have managed to stay in power.
Macron’s government is expected to survive a no-confidence vote after the head of the conservative Republicans party in the opposition said it would vote with the president’s allies, which are 39 seats short of a majority in the 577-seat assembly.
Daily newsletter
Receive essential international news every morning
Subscribe
But the anger on the streets is likely to undermine the very purpose of his pension reform. Raising the retirement age, Macron noted, was necessary to make the French economy more competitive and in tune with the rest of the developed world, where people are living longer and healthier lives with security benefits threatening to put budgets into deficits.
However the social fallout of Macron’s latest political gamble is unlikely to increase France’s economic competitiveness while highlighting its exceptionalism as a country deeply committed to maintaining the existing official retirement age.
By Thursday night, thousands of protesters had gathered on Place de la Concorde, across the river Seine from parliament. Police fired tear gas as angry demonstrators hurled cobble stones at security officers. In several other French cities, including Marseille, there were also spontaneous protests against the reform.
French unions called for another day of strikes and action against the reform on Thursday, March 23.
It was just one sign of things to come, according to Herbert. “If you thought things were already tense in France over the past couple of weeks, couple of months, stand by, because passions are about to be even more inflamed,” he warned.